Have you ever wondered whether your car’s air conditioning system uses gas or electricity? Well, here’s a surprising fact for you: air conditioning in cars primarily runs on electricity! Despite being vital for cool and comfortable drives, the air conditioning system does not rely on gasoline or any other form of fuel. Instead, it draws electric power from the car’s battery or alternator to operate.
The use of electricity in car ac systems has a significant history. In the early days, air conditioning was a luxury feature only found in high-end vehicles. However, with advancements in technology and increasing customer demand, air conditioning systems became more common in cars. Today, air conditioning accounts for nearly 5% of a car’s total fuel consumption.
Despite this energy consumption, modern car manufacturers are continuously striving to improve the efficiency of air conditioning systems, introducing innovative features such as automatic temperature control and eco-mode to minimize fuel usage and environmental impact.
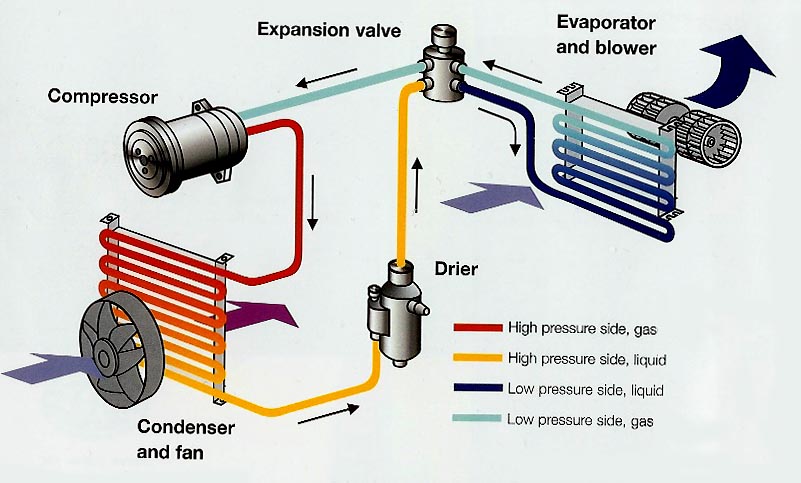
Table of Contents
ToggleDoes Air Conditioning Use Gas or Electricity in a Car?
When it comes to cooling down your car on a hot summer day, air conditioning is a must-have feature. But have you ever wondered whether your car’s air conditioning system runs on gas or electricity? In this article, we will explore and debunk the common misconceptions surrounding this topic. Let’s dive in and find out the truth about how ac works in a car.
Understanding the Basics of Car Air Conditioning
Car air conditioning systems are designed to provide relief from heat and humidity by cooling down the air inside the vehicle. However, many people believe that air conditioning in cars operates similarly to home air conditioning units, using electricity to power the cooling mechanism. In reality, car air conditioning systems rely on a combination of electricity, mechanical power, and a refrigerant gas to function.
The process begins with the compressor, which is typically powered by the car’s engine and is responsible for pressurizing the refrigerant gas. Once pressurized, the gas flows to the condenser, where heat is expelled, causing the gas to liquefy.
The liquid refrigerant then travels through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature. As the refrigerant evaporates, it absorbs heat from the air, cooling it down. Finally, the cool air is blown into the car’s cabin through the air vents. Throughout this process, both electricity and gas play important roles.
While the air conditioning system requires electricity to power the compressor, the cooling itself is primarily achieved through the interaction between the refrigerant gas and the surrounding air. So, to answer the question, car air conditioning relies on both gas and electricity to keep you cool and comfortable on the road.
The Role of Refrigerant Gas in Car Air Conditioning
Now that we understand the importance of refrigerant gas in car air conditioning, let’s take a closer look at its role in the cooling process. Refrigerant gas is the medium through which heat is transferred and removed from the inside of the vehicle.
One commonly used refrigerant in car air conditioning systems is called R-134a. This colorless gas has excellent thermodynamic properties, making it an ideal choice for cooling applications. As the refrigerant passes through the different components of the air conditioning system, it undergoes phase changes from gas to liquid and back to gas. This allows it to absorb heat from the air inside the car and release it outside, effectively lowering the temperature and creating a cooler environment.
It’s important to note that refrigerant gases, including R-134a, have been found to contribute to climate change when released into the atmosphere. To minimize environmental impact, it is crucial to handle and dispose of refrigerants properly, ensuring they do not leak or contaminate the air.
Gasoline-Powered vs. Electric Cars: Impact on Air Conditioning
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), some may wonder if there are any differences in how air conditioning works in gasoline-powered cars compared to electric cars. In terms of cooling performance and functionality, there is no significant difference between the two.
While gasoline-powered cars generate electricity through their alternators to power the air conditioning system, electric cars utilize power from their battery packs. This means that while the energy source may vary, the end result is the same – a cool and comfortable cabin for the occupants.
However, it’s worth noting that running the air conditioning in an electric car may have a greater impact on battery range compared to gasoline-powered vehicles, as it draws power directly from the battery pack.
Modern advancements in automotive technology and the shift towards sustainability have led to the development of more efficient air conditioning systems that minimize energy consumption and reduce environmental impact.
As electric vehicles become more prevalent, manufacturers are continuously improving the efficiency of air conditioning systems to optimize range and ensure a comfortable driving experience.
Benefits of Air Conditioning in Cars
Now that we understand how air conditioning in cars works, let’s take a look at the benefits it provides:
- Comfort: Air conditioning keeps the interior of your car cool, allowing you to enjoy a comfortable driving experience, especially during hot weather.
- Safety: A cool and comfortable cabin helps prevent fatigue, which can improve driver focus and reduce the risk of accidents.
- Health: Air conditioning helps filter and purify the air inside the car, reducing the presence of allergens and pollutants, which is beneficial for those with allergies or respiratory conditions.
- Resale Value: Cars equipped with air conditioning systems tend to have higher resale values, as this feature is highly sought after by buyers.
- Versatility: In addition to cooling, some car air conditioning systems also provide heating capabilities, ensuring optimal comfort regardless of the outside temperature.
Tips for Optimal Use of Car Air Conditioning
To maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your car’s air conditioning system, consider the following tips:
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance checks to ensure that the system is functioning properly and to address any potential issues before they become major problems.
- Proper Use of Recirculation Mode: Use the recirculation mode sparingly, as it can cause a buildup of humidity inside the car, leading to fogged windows and discomfort.
- Avoid Extreme Temperature Settings: Instead of setting the temperature to the lowest possible level, use a moderate setting that provides comfort without putting excessive strain on the system.
- Allow for Ventilation: Occasionally, open the windows or sunroof to allow fresh air to circulate through the cabin, reducing reliance on the air conditioning system.
- Park in Shade: Whenever possible, park your car in shaded areas or use windshield shades to reduce the amount of direct sunlight entering the vehicle, minimizing the need for intense air conditioning.
Air Conditioning: Powering Comfort on the Road
Car air conditioning systems rely on a combination of gas and electricity to keep you cool and comfortable while driving. Understanding how these components work together is key to maintaining optimal performance and efficiency. Whether you drive a gasoline-powered car or an electric vehicle, the cooling process remains the same.
As advancements in technology continue to shape the automotive industry, air conditioning systems will undoubtedly become even more efficient and sustainable in the future.
Key Takeaways: Does air conditioning use gas or electricity in a car?
- A car’s air conditioning system primarily uses electricity to function.
- The air conditioner’s compressor is powered by the car’s engine, which is fueled by gasoline.
- However, the electricity necessary to operate the air conditioning system is generated by the car’s alternator, which is driven by the engine.
- Using the air conditioning system in a car can slightly decrease the fuel efficiency, as it requires the engine to work harder.
- Regular maintenance and servicing of the air conditioning system are important to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Air conditioning in a car is a vital feature that keeps you cool and comfortable during hot summer drives. To understand how it operates, let’s dive into some of the common questions related to whether air conditioning in a car uses gas or electricity.
How does the air conditioning system in a car work?
The air conditioning system in a car works by using a combination of mechanical and electrical components. It starts by compressing a refrigerant gas, usually called R134a, using a belt-driven compressor powered by the engine. This compression increases the temperature and pressure of the gas, turning it into a high-pressure, high-temperature vapor.
The vapor then flows through a condenser, which is located in front of the car’s radiator. As air passes over the condenser, it removes heat from the vapor, causing it to condense into a high-pressure liquid. This liquid then goes through an expansion valve, where it rapidly expands, reducing its pressure and temperature.
Finally, the cold refrigerant flows through an evaporator, which is located inside the car’s cabin, and as air passes over it, it absorbs heat, cooling down the air that is blown into the cabin by the car’s blower fan.
Does the car’s air conditioning system use gas?
Yes, the air conditioning system in a car uses a refrigerant gas to cool the air. This refrigerant gas is responsible for the cooling cycle that is essential in air conditioning. However, it’s important to note that this gas is not the same as the fuel used to power the car’s engine.
The refrigerant gas, usually R134a, is contained in a closed-loop system within the air conditioning system. It goes through a continuous cycle of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation, absorbing and releasing heat in the process.
So while the AC system uses gas, it does not consume it like the engine consumes fuel. The same gas is recycled within the system without being depleted or needing frequent refills.
Does the car’s air conditioning system use electricity?
Yes, the car’s air conditioning system also relies on electricity to power its components and make the cooling process possible. The belt-driven compressor, which is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas, is driven by the engine using a belt connected to the engine’s crankshaft. This mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy by the compressor.
In addition, other electrical components, such as the blower fan, control switches, sensors, and the car’s electrical system, play a crucial role in the operation of the air conditioning system. These components require electricity to function properly and provide the desired cooling effect in the cabin of the car.
Does using the air conditioning system in a car consume more fuel?
Using the air conditioning system in a car does put an additional load on the engine, which can lead to increased fuel consumption. When the air conditioning is turned on, the engine needs to work harder to power the compressor and generate the cool air for the cabin. This increased workload on the engine can result in a higher fuel consumption rate.
However, the extent of the impact on fuel consumption may vary depending on various factors such as the type of car, driving conditions, and the efficiency of the air conditioning system itself.
In some cases, the impact may be minimal, while in others, it can be noticeable. To optimize fuel efficiency, it’s recommended to use the air conditioning system judiciously and consider using other cooling methods, such as rolling down the windows or utilizing airflow from outside when feasible.
Can you run the car’s air conditioning while the engine is off?
In most conventional cars, the air conditioning system is directly powered by the engine, which means that it can only function when the engine is running. When the engine is turned off, the compressor stops receiving power, and the air conditioning system will not operate.
However, in some modern hybrid or electric vehicles, there may be a function called “pre-conditioning” that allows you to cool or warm up the car’s interior before starting your journey. This feature uses the vehicle’s battery or hybrid system to power the air conditioning system when the engine is off, enabling you to enjoy a comfortable cabin temperature even before setting off.
VERIFY: Does Not Using AC in Your Car Save Gas?
To sum up, we talked about staying flexible in a rapidly changing world. We explored the value of learning new skills and adapting to different situations. It’s important to be open-minded and embrace new opportunities as they arise.
Remember, change can be scary, but it also brings growth and new possibilities. So, keep an open mind and be ready to adapt. Life is an adventure full of unexpected twists and turns, and staying flexible will help you navigate through it successfully. Keep learning, keep growing, and keep embracing change!
In conclusion, we discussed the importance of staying flexible and embracing change. Life is a journey filled with unexpected events, and being adaptable allows us to navigate through challenges and seize opportunities.
By embracing new skills and remaining open-minded, we can thrive in a rapidly changing world. Change may seem daunting, but it also brings growth and new possibilities. So, keep an open mind, be ready to adapt, and embrace the adventure of life!









